Features and Mechanism
Features and product lineup of seismic dampers for buildings
Overview of Sumitomo Rubber's seismic dampers
In Japan, where earthquakes occur frequently, safety and comfort are further enhanced by the seismic control technology “GRAST”.
Sumitomo Rubber's seismic dampers for buildings make full use of the outstanding properties of high-damping rubber, developed through over 100 years of tire research and development.
- Space-saving design allows for greater flexibility in building use and planning.
- Suitable for a wide range of applications—from wind-induced vibrations to major earthquakes.
- Damper device reusability and its repeated performance are effective in aftershock protection.*1
- Uses high-durability rubber, eliminating the need for regular maintenance.*2
- Proven track record not only in buildings, but also in bridge cables and residential homes.
- More cost-effective compared to other products with equivalent performance.
*1 Based on the results of repeated cycle tests conducted in August 2016 at Sumitomo Rubber Industries’ Kakogawa Plant using full-scale products.
*2 Based on the results of the accelerated deterioration test conducted by Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd.
High-damping rubber : An evolution of rubber technology
Sumitomo Rubber, with its thorough understanding of rubber properties, developed the “high-damping rubber.”
Sumitomo Rubber's compounding technology enables the full potential of rubber materials to be realized.

"High-damping rubber" born from racing tire development
Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber was developed by applying the advanced technologies cultivated over many years in the development of racing tires.
Thanks to the inherent versatility of rubber, it is used across a wide range of fields—from bridges and buildings to single-family homes.
Sumitomo Rubber's “GRAST” — Suppressing vibration by converting it into heat
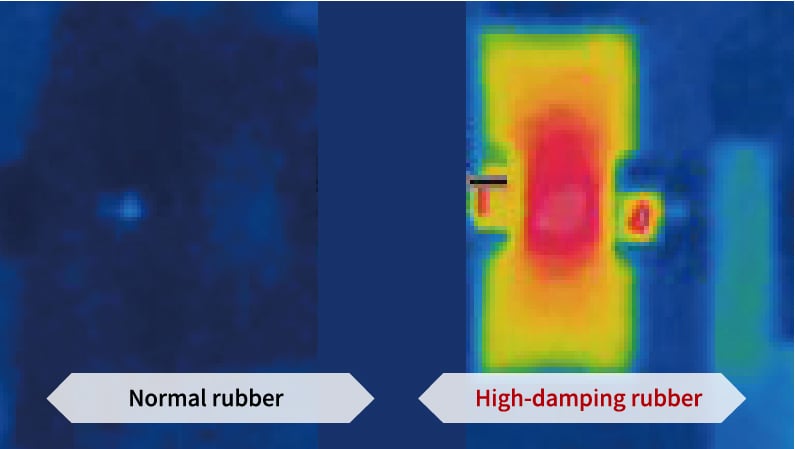
High-damping rubber is a special type of rubber that instantly converts vibration energy into heat.
Sumitomo Rubber's vibration control technology, “GRAST”, utilizes this property to significantly reduce various types of building vibrations — not only decreasing their intensity, but also shortening the duration of the shaking.
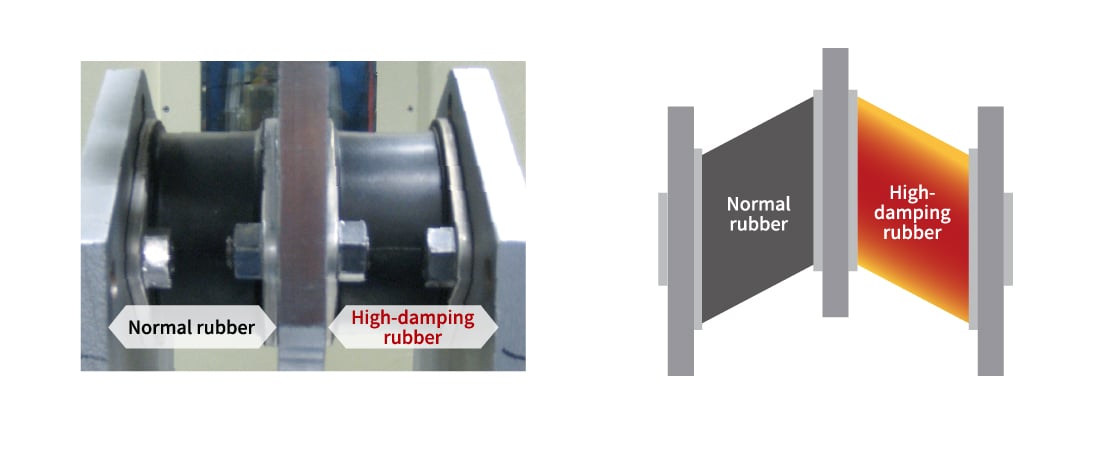
Highly effective against repeated aftershocks
One of rubber's greatest strengths is its ability to perform repeatedly without losing effectiveness.
Sumitomo Rubber's seismic dampers for buildings take full advantage of this property, delivering high damping performance even against a series of aftershocks that strike again and again.*
*Based on the results of repeated cycle tests conducted in August 2016 at Sumitomo Rubber Industries’ Kakogawa Plant using full-scale products.
Effective against wind-induced sway and traffic vibrations
One of the key features of high-damping rubber is its ability to absorb energy even at small amplitudes. Thanks to this properties, we have an extensive track record in the field of cable dampers for bridges, where it has proven effective in suppressing cable vibrations. Its performance in mitigating even minor vibrations such as wind-induced sway has been well demonstrated.
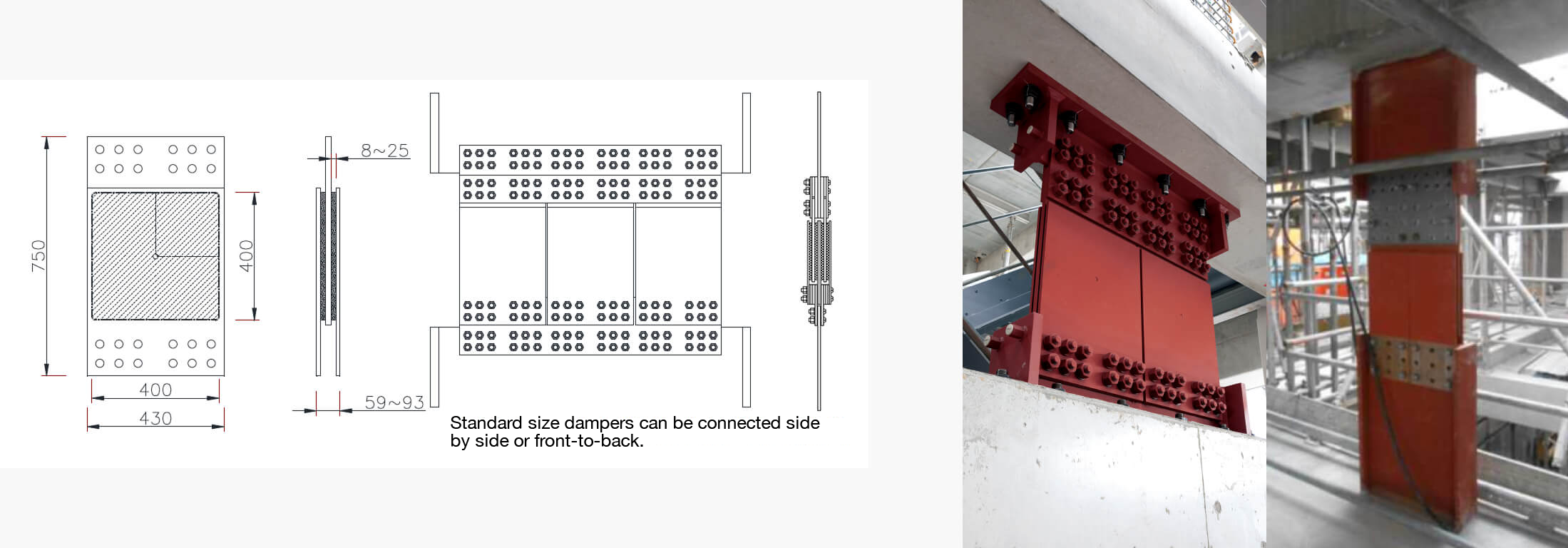
Rubber dimensions: 80mm in diameter, 40 mm thickness
Test conditions: 0.5Hz, 20℃, ±20mm
*The temperature remains below the ignition point even during heat dissipation.
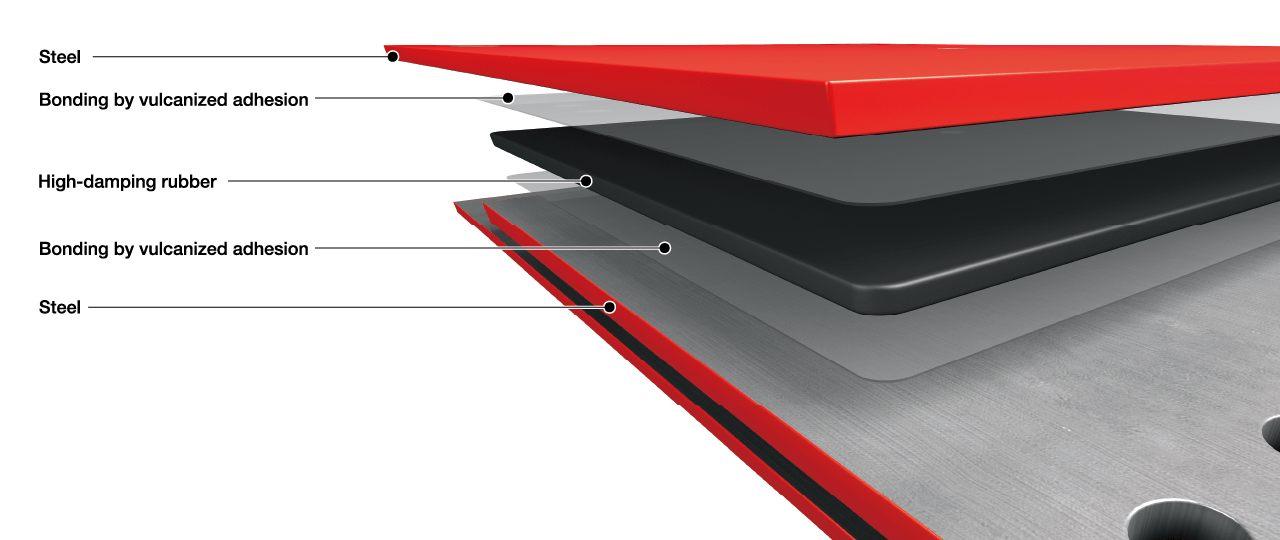
System cross-sectional view
Vulcanized adhesion is used to join the steel plates and high-damping rubber. A two-layer adhesive structure is adopted, utilizing one adhesive compatible with rubber and another compatible with steel. Through chemical reactions, this ensures a strong and durable bond. Accelerated aging tests under heat have confirmed that the performance remains virtually unchanged even after the equivalent of 60 years, maintaining its effectiveness. *
*Based on the results of the accelerated deterioration test conducted by Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd.
Sumitomo Rubber's high damping rubber
Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber combines high initial stiffness with excellent damping performance, making it effective even against micro-vibrations.
“GRAST” is effective not only for major earthquakes and aftershocks but also for small vibrations such as wind sway and long-duration shaking caused by long-period seismic waves, solving various building vibration issues.
Realizing building dampers effective even against micro-vibrations.
With a simple damper design that reduces backlash, the structure effectively leverages the performance of high-damping rubber, making it highly effective even for micro-vibrations. It is widely applicable, from steel-frame and concrete buildings to both super high-rise and small-to-medium scale structures.
Achieving cost reduction
The use of high-stiffness high damping rubber allows a more compact design of building dampers, leading to cost reduction per unit.
Moreover, since the damper capacity can be adjusted according to design targets, it has the potential to reduce the overall expenditure on vibration control devices.
In addition, its excellent durability against repeated stress and long-term performance stability eliminate the need for regular maintenance.*
*Based on the results of the accelerated deterioration test conducted by Sumitomo Rubber Industries, Ltd.
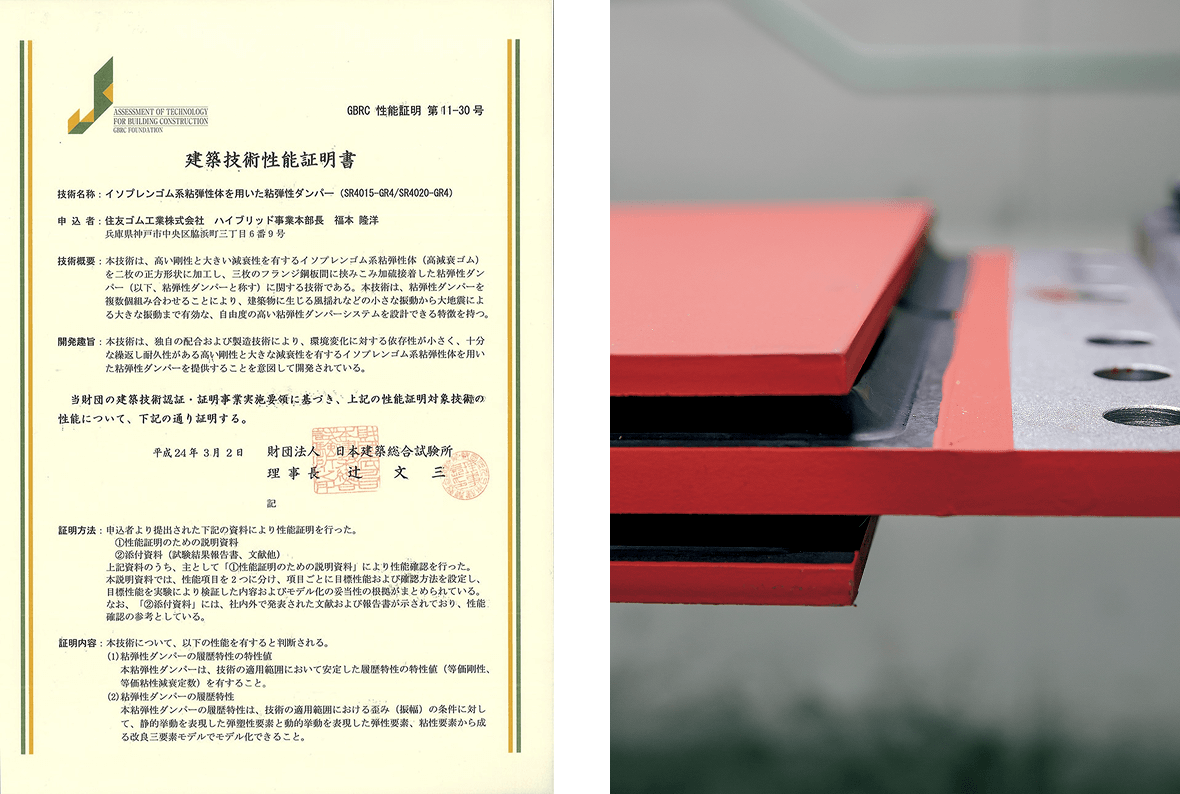
Obtained architectural technology performance certification from an official institution
At Sumitomo Rubber, various performance aspects of building dampers have been verified through full-scale testing.
In addition, we have developed high-precision modeling to enable seismic response analysis of buildings equipped with these dampers.
By conceptualizing the damper as an assembly of multiple components rather than a single element, the analysis accuracy has been significantly improved compared to models based on a single element.
In March 2012, we obtained architectural technology performance certification for both the damper performance and its modeling.
Comparison of material stress with other products
Comparison among different vibration dampers
Vibration control dampers enhance the safety of buildings and apartments. They are effective not only against strong shaking but also for mitigating micro-vibrations such as long-period seismic waves and wind-induced sway.
There are several types of vibration dampers, and we have compared their effectiveness in earthquake mitigation as well as various dependency factors.*
*Regarding the damper models of both our company and other companies used for the comparison, the information is based on publicly available sources
(Manual for Design and Construction of Passively-Controlled Buildings, 3rd Edition, etc.)
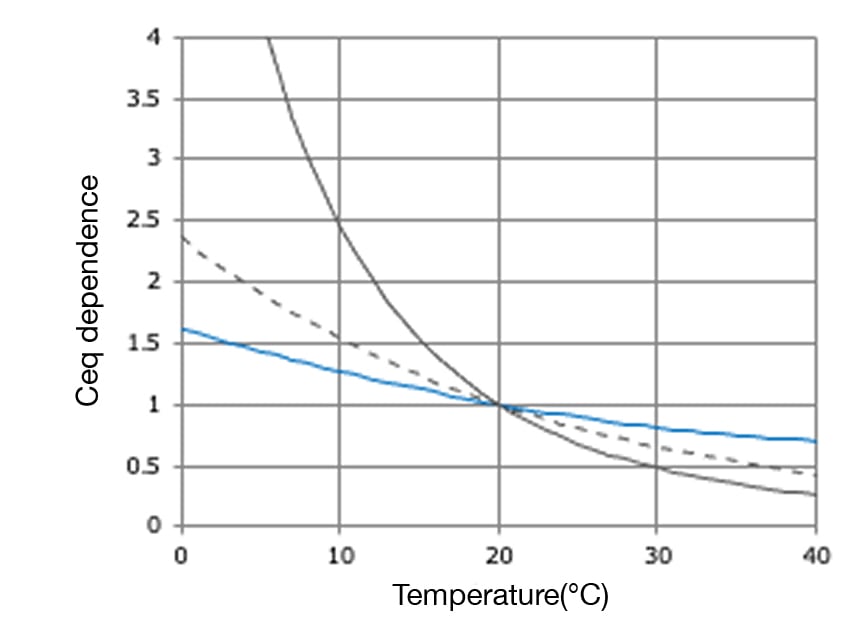
Comparison of temperature dependence
Compared to conventional viscoelastic dampers and other types of dampers, it features low temperature dependence, making design easier.
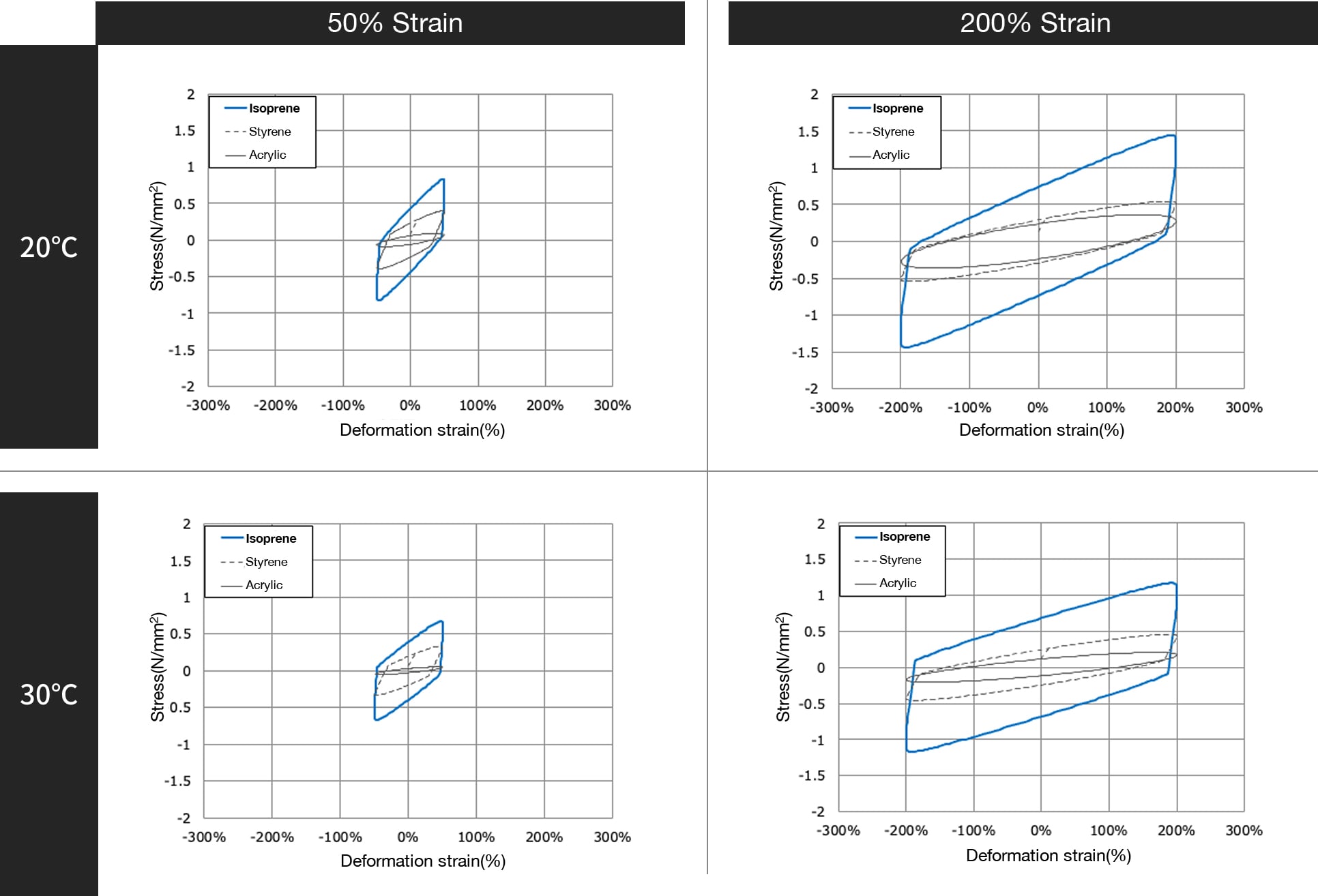
Comparison of material stress under 0.5 Hz excitation
Differences in viscoelastic materials — comparison of material stress
Sumitomo Rubber's vibration dampers use isoprene-based materials.
Since isoprene materials have high energy absorption per unit volume, they enable the downsizing of vibration control devices.
Comparison of material stress under 0.5 Hz excitation
Furthermore, isoprene materials have low dependence on frequency and temperature, offering ease of design.

Lineup
Sumitomo Rubber's building vibration dampers offer flexible solutions that can be implemented without being constrained by site conditions or cost, ideal for the increasing prevalence of high-rise buildings.
By combining multiple unites instead of using a single damper, the capacity per damper location can be adjusted.

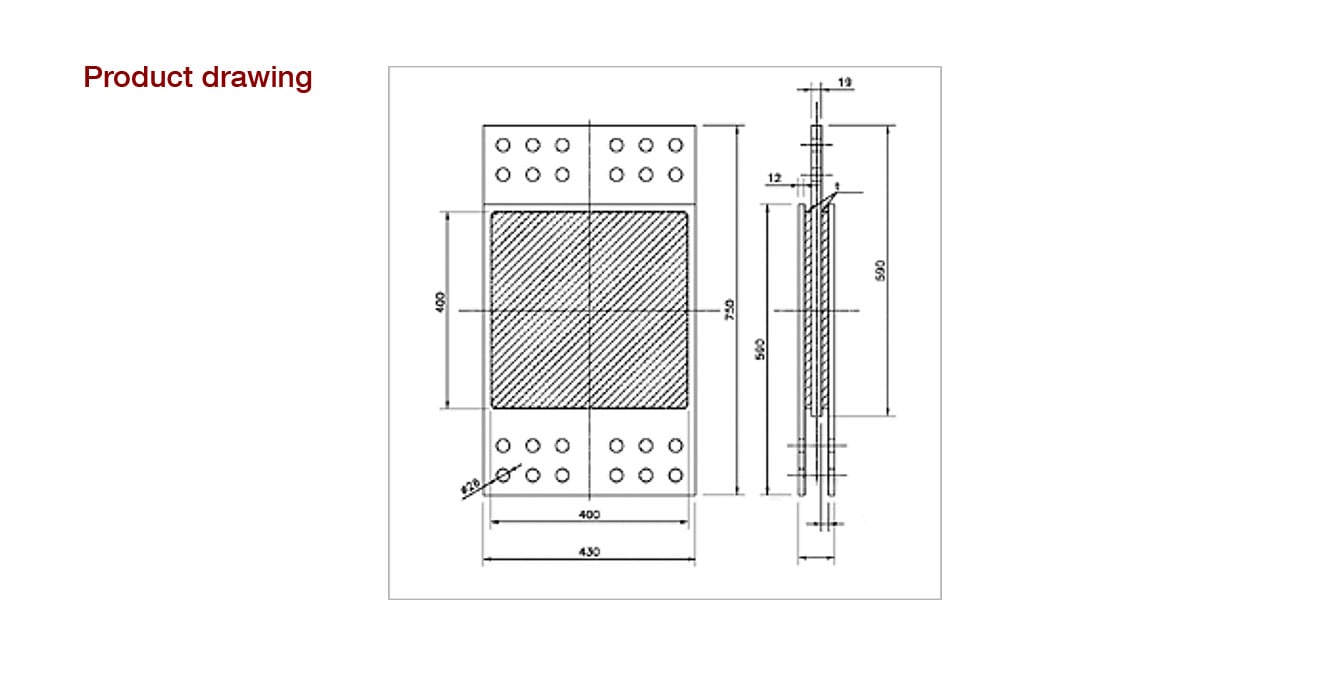
| Product name | Dimension of the high damping rubber | Allowable deformation (mm) | Maximum shear force* (kN) | Ultimate deformation (mm) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cross section area (cm²) | Thickness (mm) | ||||
| SR3315-GR4 | 2240 | 15 | 30 | 280 | 45 |
| SR4008-GR4 | 3200 | 8 | 16 | 400 | 24 |
| SR4015-GR4 | 15 | 30 | 45 | ||
| SR4020-GR4 | 20 | 40 | 60 | ||
| SR4025-GR4 | 25 | 50 | 75 | ||
| SR4420-GR4 | 3872 | 20 | 40 | 484 | 60 |
*At 200% shear strain, 0.1Hz frequency, and 20℃
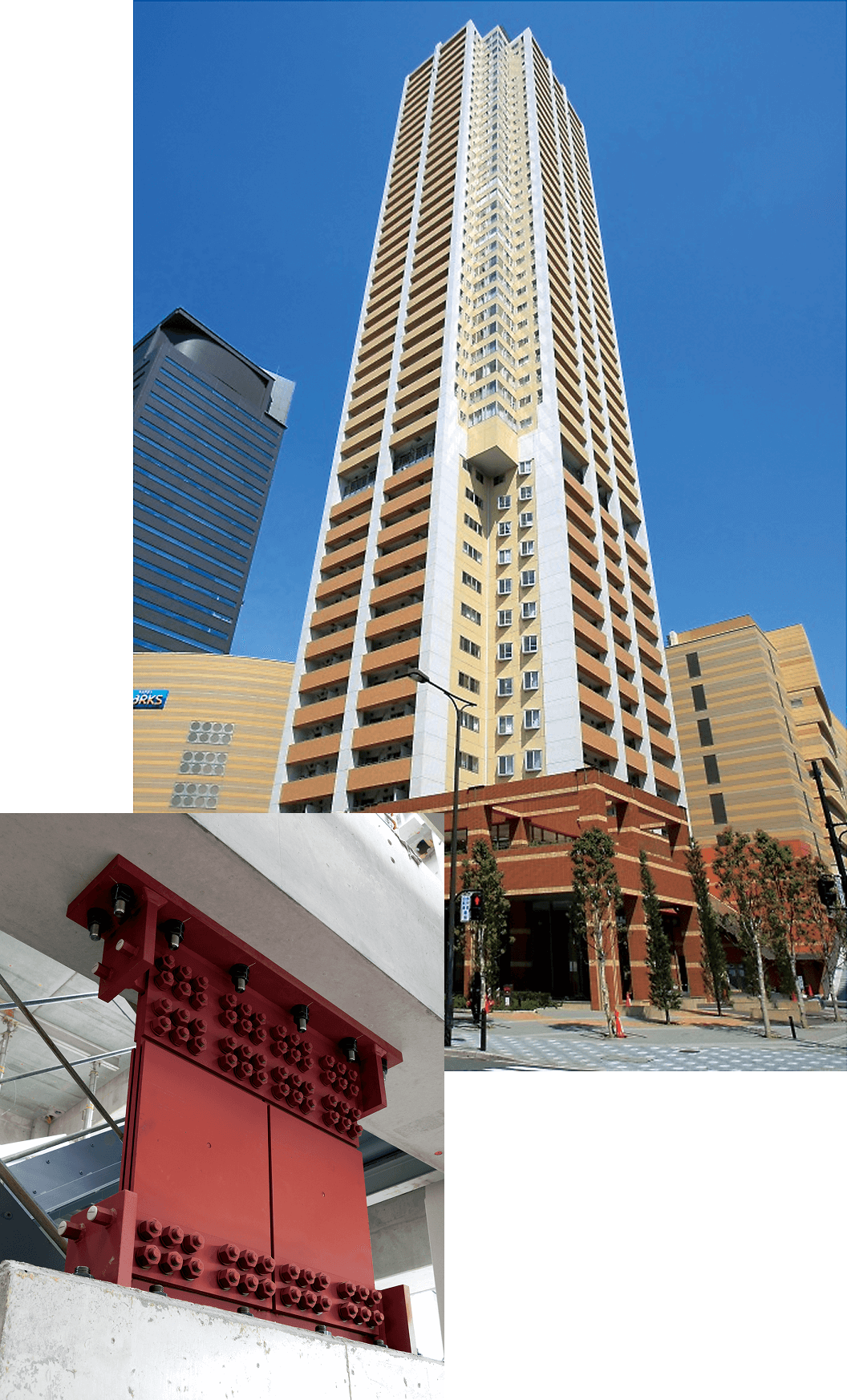

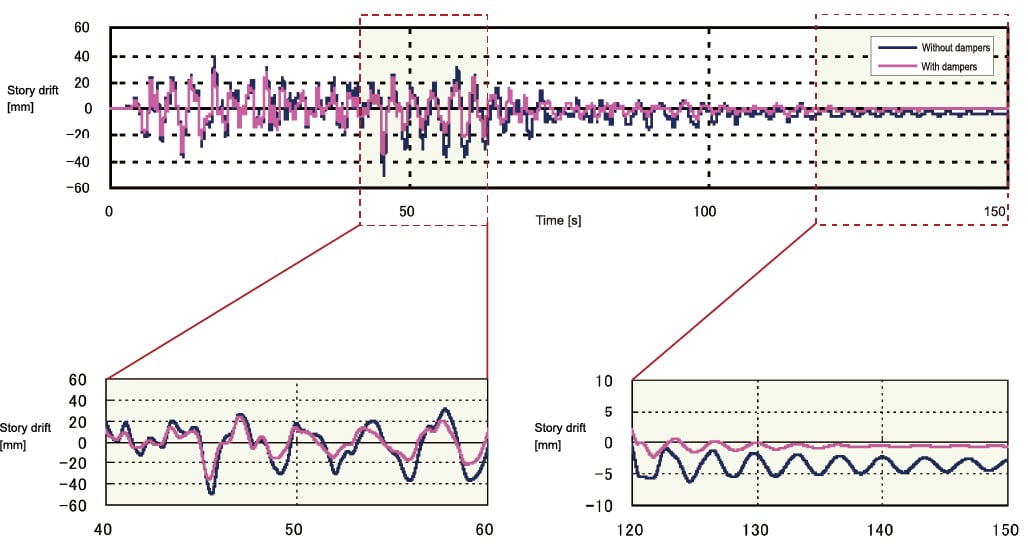
Case study on installation effectiveness
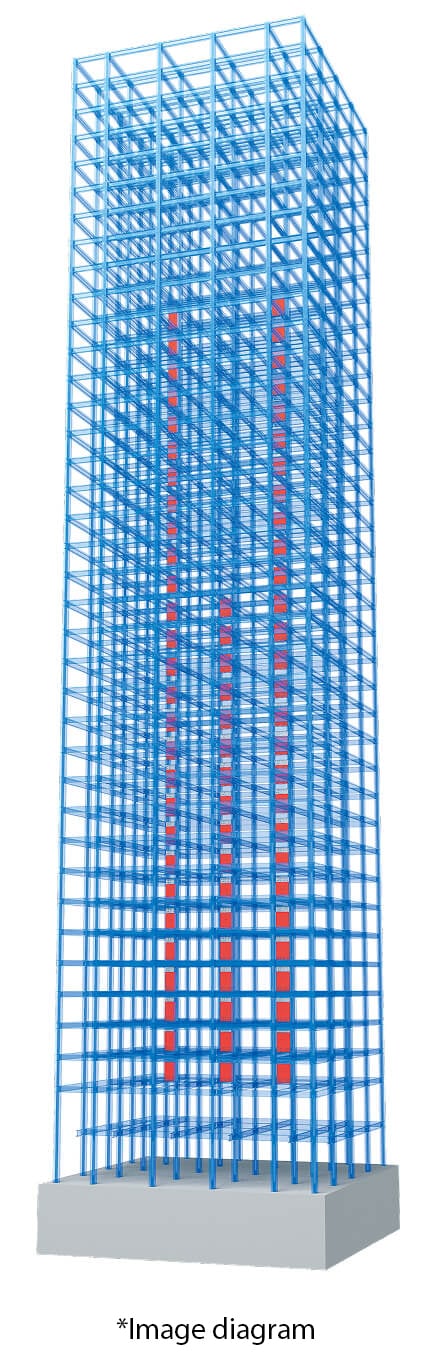
| Building model | 30-story lumped-mass model |
|---|---|
| Structure | Steel structure |
| Floor plan geometry | 30×30 ㎡ |
| Height | 120m |
|---|---|
| Input seismic wave | BCJ(Level 1 / Level 2) |
Damper arrangement
| Story | Number of installed dampers |
|---|---|
| 30 | 2 |
| 29 | 2 |
| 28 | 2 |
| 27 | 2 |
| 26 | 2 |
| 25 | 4 |
| 24 | 6 |
| 23 | 6 |
| 22 | 6 |
| 21 | 6 |
| Story | Number of installed dampers |
|---|---|
| 20 | 6 |
| 19 | 6 |
| 18 | 6 |
| 17 | 6 |
| 16 | 6 |
| 15 | 6 |
| 14 | 4 |
| 13 | 4 |
| 12 | 2 |
| 11 | 2 |
| Story | Number of installed dampers |
|---|---|
| 10 | 0 |
| 9 | 2 |
| 8 | 2 |
| 7 | 2 |
| 6 | 2 |
| 5 | 2 |
| 4 | 2 |
| 3 | 2 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 1 | 2 |
| Total | 104 |
*Results based on analyses performed by Sumitomo Rubber Industries using the structural analysis software SNAP (KOZO SYSTEM, INC.)