What is “GRAST”?
“GRAST”, Sumitomo Rubber's vibration control technology, helps create a safer and more comfortable life.
“GRAST” is Sumitomo Rubber's vibration control technology that utilizes high-damping rubber. When deformed by shaking, this rubber converts kinetic energy into heat. By harnessing this property, “GRAST” helps absorb and control a wide range of vibrations—from minor movements caused by wind to large seismic motions—thereby supporting a safer and more comfortable living environment.
Key features of Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping seismic dampers
- We offer a range of existing products for various applications, including bridges, buildings, and residential houses.
- Capable of reducing various types of vibrations, from small-scale shaking to large-scale seismic activity.
- Suitable for various types of buildings, from short- to long-period structures.
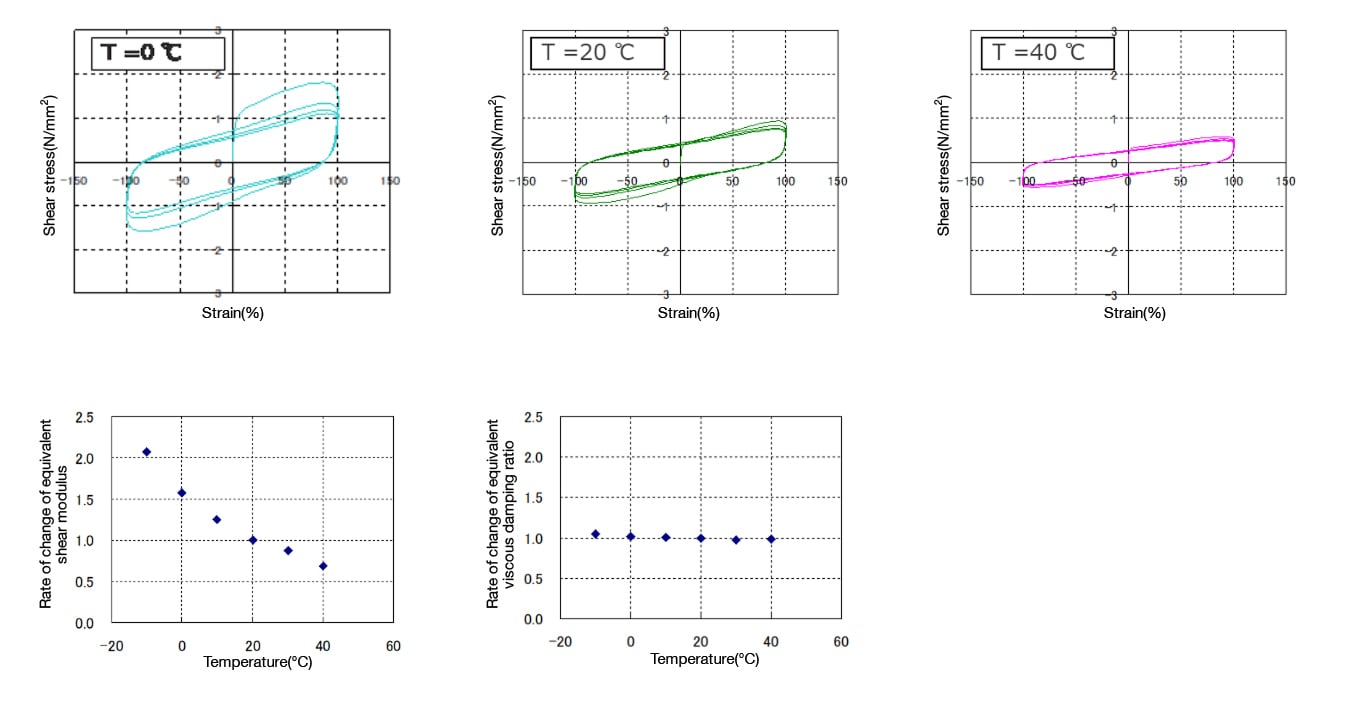
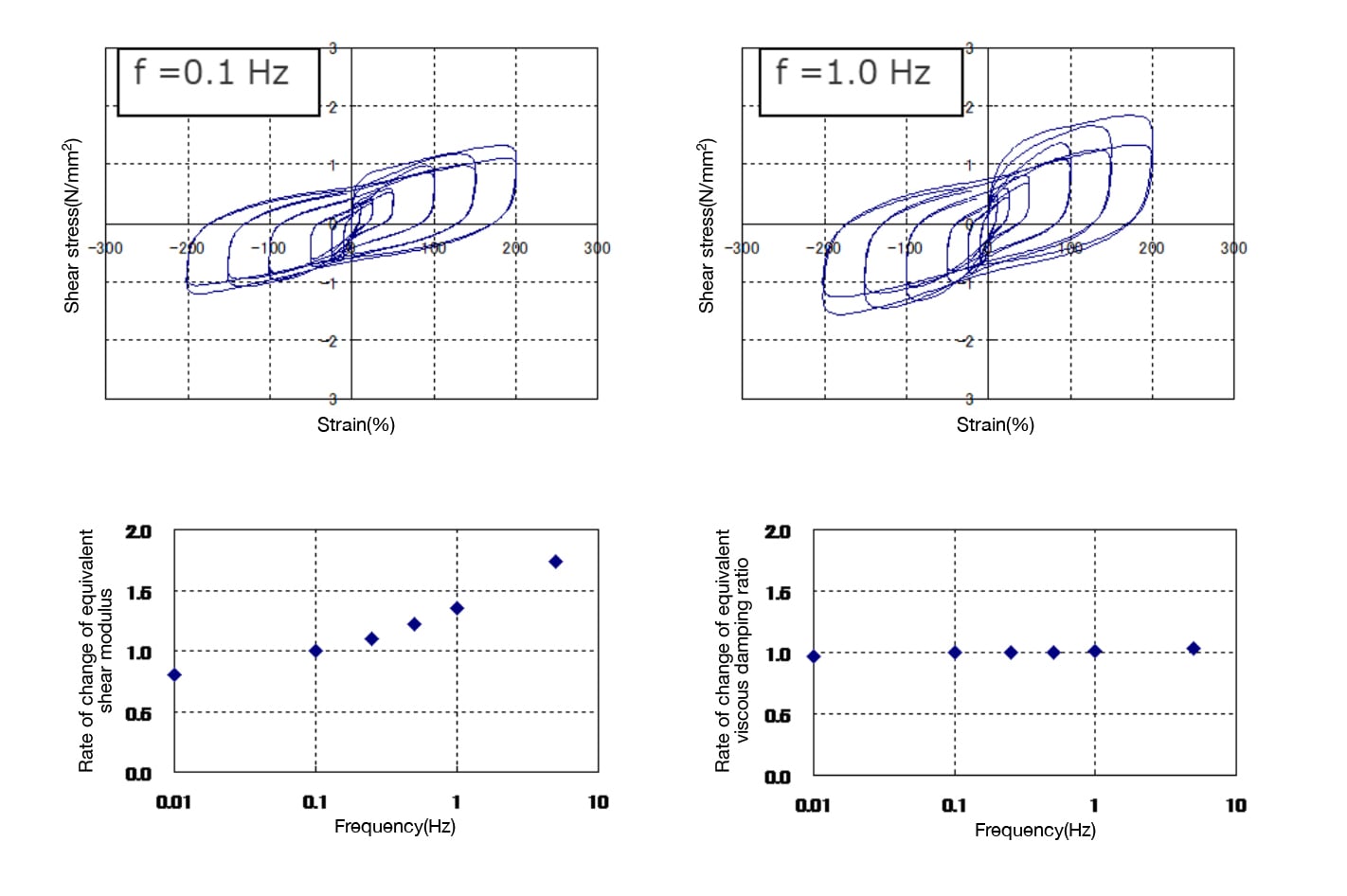
- Exhibits stable damping performance with minimal temperature dependence across a wide range from -20°C to 60°C.
- Due to its high rigidity, it exhibits excellent damping capacity despite its compact size.
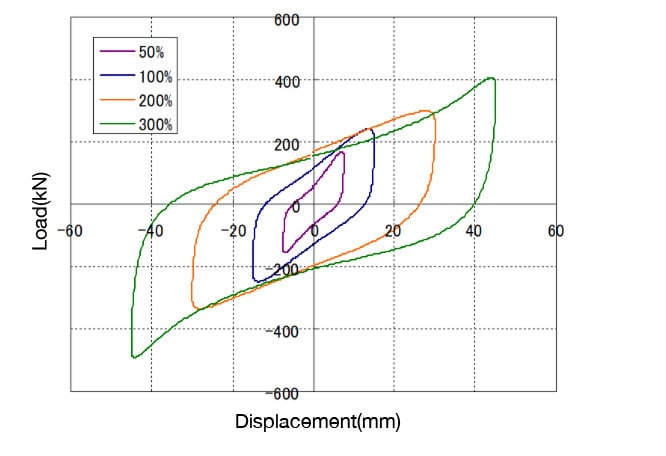
- Tests have demonstrated that it shows minimal performance degradation even after repeated use.*
- The simple structure facilitates straightforward installation and maintenance.
*Based on the results of repeated cycle tests conducted in August 2016 at Sumitomo Rubber Industries’ Kakogawa Plant using full-scale products.
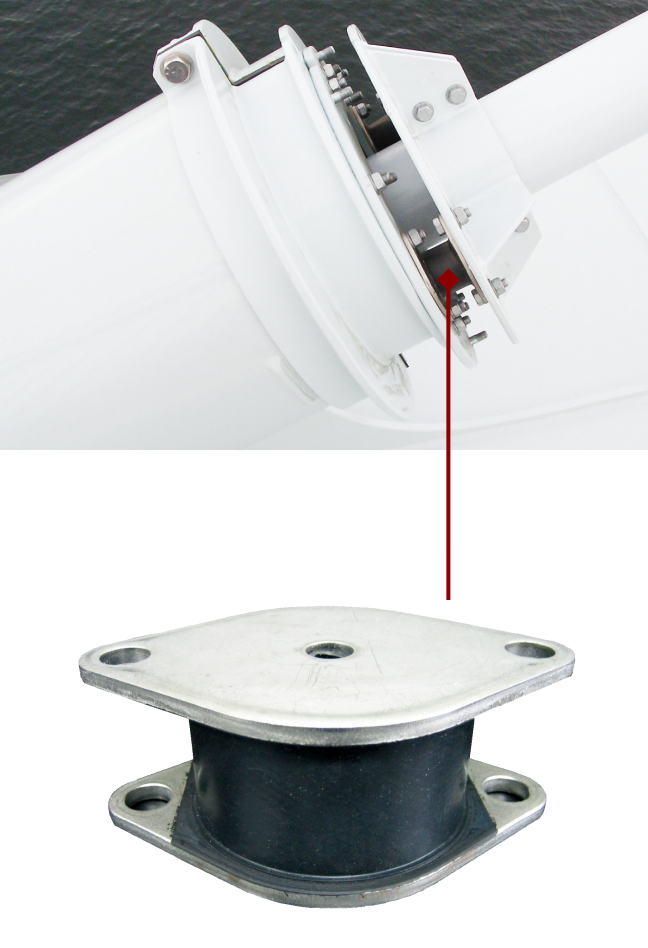
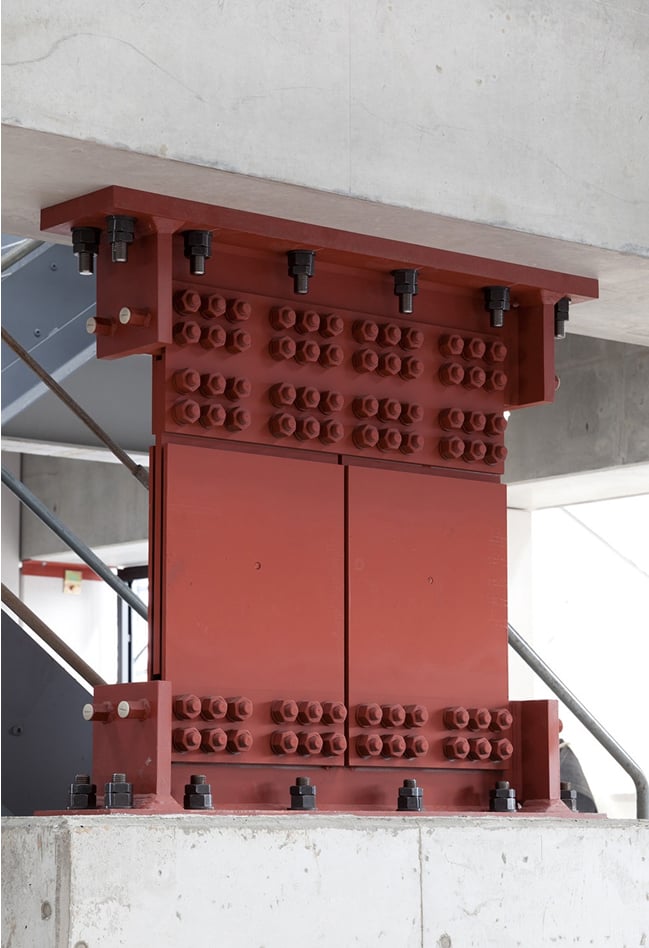
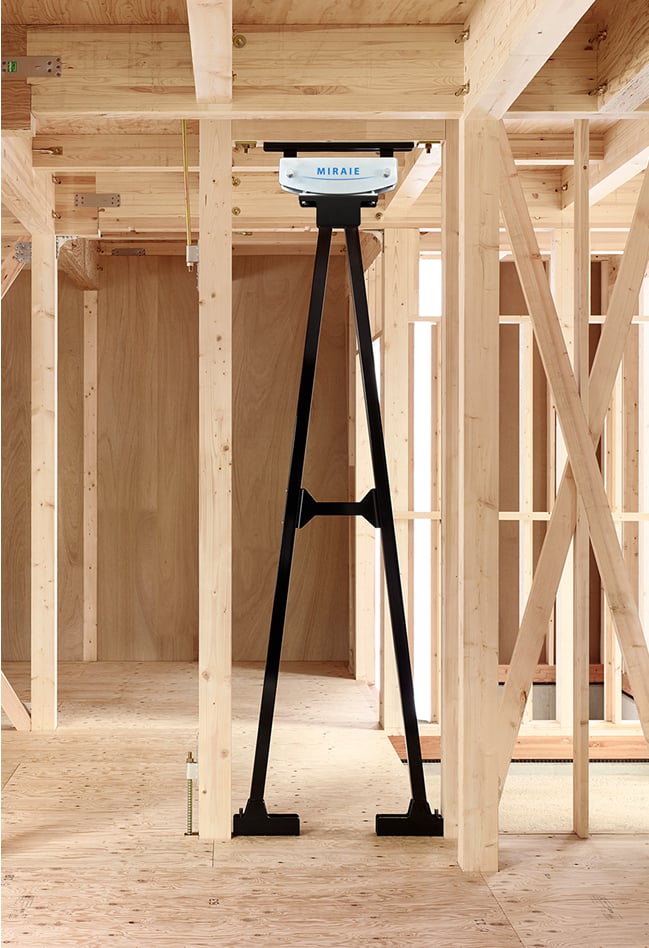



Characteristic of High-damping rubber
What is High-damping rubber
High-damping rubber is a type of rubber material that is engineered to offer greater energy absorption (damping) performance than ordinary rubber.
It absorbs and dissipates vibrational energy by converting it into heat when deformed, such as during an earthquake.
Performance of High-damping rubber
Why can high-damping rubber exhibit such high damping capacity? The answer lies in its special formulation of the high-damping rubber. This formulation enhances the three key components of a viscoelastic material: the viscous damping element, the spring element (elastic element), and the friction damping element, enabling the rubber to achieve high damping performance.
Technical data
 We have obtained a Building Technology Performance Certificate.
We have obtained a Building Technology Performance Certificate.
Sumitomo Rubber's viscoelastic damper for buildings have obtained a Building Technology Performance Certificate from the General Building Research Corporation of Japan (GBRC).
Content of the certificate
(1) Hysteretic characteristic of viscoelastic dampers
This viscoelastic damper possesses stable hysteretic properties (equivalent stiffness and equivalent viscous damping ratio) within the applicable range of the technology.
(2) Modeling of viscoelastic damper
The hysteretic behavior of this viscoelastic damper can be modeled as an modified three-element model (plastic element, elastic element, and viscous element) under the conditions of strain (amplitude), temperature, and frequency within the applicable range of the technology.
*The model is incorporated into general dynamic analysis software such as SNAP (KOZO SYSTEM, INC.), SS21/dynamic PRO, 3D dynamic (UNION SYSTEM Inc.), MIDAS iGen (MIDAS IT), RESP-D/F3T (KOZO KEIKAKU ENGINEERING Inc.), ETABS, and SAP2000 (COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES, INC.).
Improvements in seismic performance and comfort verified through joint research with Kyoto University.
From 2005 to 2023, we conducted joint research with the Laboratory of Geotechnical and Geoenvironmental Engineering, Department of Architecture and Architectural Engineering, Graduate School of Engineering, Kyoto University.
In this collaborative research, we have examined the reduction effects on seismic and wind responses when incorporating Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber into high-rise buildings. These effects have been verified through experimental studies, such as dynamic loading tests under extremely small deformations, as well as theoretical studies, such as equivalent linear analysis. The research has clarified that it is possible to achieve a well-balanced reduction of acceleration responses related to habitability and displacement responses related to structural safety, covering a wide range from small wind disturbances that occur constantly to extremely rara large earthquakes." (1)(2)
(1) Seikou Tsuji, Tsubasa Tani, Izuru Takewaki, and Tatsuji Matsumoto: Improvement of occupancy performance of buildings by high-hardness rubber viscoelastic dampers, proceedings of the 12th Japan earthquake engineering symposium CD-ROM, pp.970-973 (2006)
(2) Seikou Tsuji, Tsubasa Tani, Chihiro Suzuki, Shinta Yoshitomi, Izuru Takewaki, and Tatsuji Matsumoto: Added damping at very small amplitude by high-hardness rubber dampers for reduction of building response to wind, proceedings of the 56th conference on theoretical and applied mechanics (2007)
Collaborative research with universities and other institutions
Our company is engaged in collaborative research with universities, major manufacturers across various industries, and other sectors, aiming to further advance and widely disseminate our high-damping technology, "GRAST." As a result of these efforts, practical applications have progressed in a variety of fields, including vibration control devices for high-rise buildings and detached houses, as well as seismic racks for computers. Moving forward, we will continue to pursue the limitless potential of "GRAST" through joint research with many partners.
Research content
In joint research conducted from 2005 to 2023 with Professor Takewaki’s Laboratory, Department of Architecture and Architectural Engineering, Kyoto University Graduate School, we examined the effectiveness of incorporating Sumitomo Rubber's high damping rubber vibration control material into high-rise buildings for reducing seismic and wind responses. Through experimental studies—such as dynamic loading tests under extremely small deformations of high damping rubber—and theoretical studies, including equivalent linear analysis, we verified that the material can effectively reduce both acceleration responses, which relate to habitability, and displacement responses, which relate to structural safety, over a wide range of conditions—from minute wind-induced vibrations occurring continuously to large-scale earthquakes.
The research clarified that it is possible to achieve a well-balanced reduction of acceleration responses related to habitability and displacement responses related to structural safety over a wide range, from minor wind disturbances acting constantly to large earthquakes that occur very rarely.
Furthermore, the characteristics of the high-damping rubber formulated through this joint research have been incorporated into general software such as SNAP (KOZO SYSTEM, INC.), SS21/DynamicPRO (UNION SYSTEM Inc.), MIDAS iGen (MIDAS IT), ETABS (COMPUTERS & STRUCTURES, INC.), and others, and are being used by many structural design professionals.
Collaborative researcher

Professor Emeritus, Kyoto University (Structural engineering) , Ph.D. in Engineering
I believe the appeal of Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber dampers lies in three main points:
(1) They can absorb large amounts of energy even from extremely small amplitudes, making them highly effective against the winds that frequently occur in daily life.
(2) Their dependency on temperature and frequency is incomparably lower than that of other products, which makes them very convenient to use in structural design.
(3) It is possible to freely create damper materials with a wide range of mechanical properties.
In recent years, structural safety has become a concern due to unexpected earthquake motions, such as large-amplitude, long-duration ground motions caused by Nankai Trough Earthquakes and long-period pulses from near-fault earthquakes. I believe that Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber dampers can serve as a "stopper" in such cases.
I have observed various types of vibration control dampers over the years, and I feel that Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber dampers are an exceptional material that brings innovation to the field of vibration control structures. By further developing our joint research, I hope to make a significant contribution to society by greatly improving both the habitability and safety of high-rise buildings.

It is increasingly recognized that seismic disaster prevention and mitigation should address not only securing structural safety for very rare earthquakes from a seismic-resistance standpoint, but also enhancing a building’s post-earthquake functionality and rapid recoverability. To ensure buildings can be used safely and with confidence, in addition to reducing response by increasing structural stiffness (= seismic resistance), it is also necessary to reduce vibration quickly (= vibration control).
Sumitomo Rubber's high-damping rubber exhibits exceptionally high energy absorption performance by converting vibration energy into heat across a wide range of vibration levels, from small tremors to large-scale shaking. In addition, when this high-damping rubber is integrated into a building, it not only imparts rigidity and effectively reduces vibrations, but also helps prevent a significant decline in structural safety even if the building sustains damage during an earthquake or similar event. In this joint research, we are developing various seismic resistant device and vibration-control devices that leverage the material properties of high-damping rubber, conducting performance verification tests, and establishing design methodologies for incorporating them into buildings.
Having experienced the Great Hanshin-Awaji Earthquake and the Great East Japan Earthquake, we deeply recognize the importance of safety measures for buildings.
Drawing on the lessons learned from these two major disasters, all of us at Sumitomo Rubber have committed ourselves to the development of "GRAST"—our vibration control technology utilizing high-damping rubber materials cultivated through years of dedicated research—under the shared motto: "Stop the shaking."
Our vibration control dampers for cable-stayed bridges have been widely adopted in regions ranging from cold to warm climates, both in Japan and overseas, thanks to their outstanding durability and stable performance. In addition, the "MIRAIE" vibration control unit for residential homes, developed immediately after the Great East Japan Earthquake, demonstrates excellent seismic performance, capable of reducing building vibrations by up to 95%.* Its effectiveness was clearly proven during the 2016 Kumamoto Earthquakes, which saw two successive tremors of seismic intensity 7. To date, over 146,000 detached houses (as of the end of August 2025) have been equipped with MIRAIE and other Sumitomo Rubber residential dampers.
More recently, our technologies have been applied to a wider range of structures—including super high-rise buildings, where long-period ground motion caused by typhoons or earthquakes is a concern, and traditional buildings, where compactness and long service life are essential.
Looking ahead, we remain committed to advancing our technologies so we can continue to contribute to the safety, security, and comfort of people’s lives across various fields. We sincerely appreciate your continued support for Sumitomo Rubber's vibration control technology, "GRAST," and welcome any proposals for new areas of application.

Executive Officer
Ph.D. in Engineering
Tatsuji Matsumoto
Note: This result is based on a full-scale experiment conducted in January 2017 at the Disaster Prevention Research Institute of Kyoto University using the MIRAIE. The comparison was made on the inter-story drift (displacement) in response to the second seismic wave excitation equivalent to seismic intensity 7.